A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
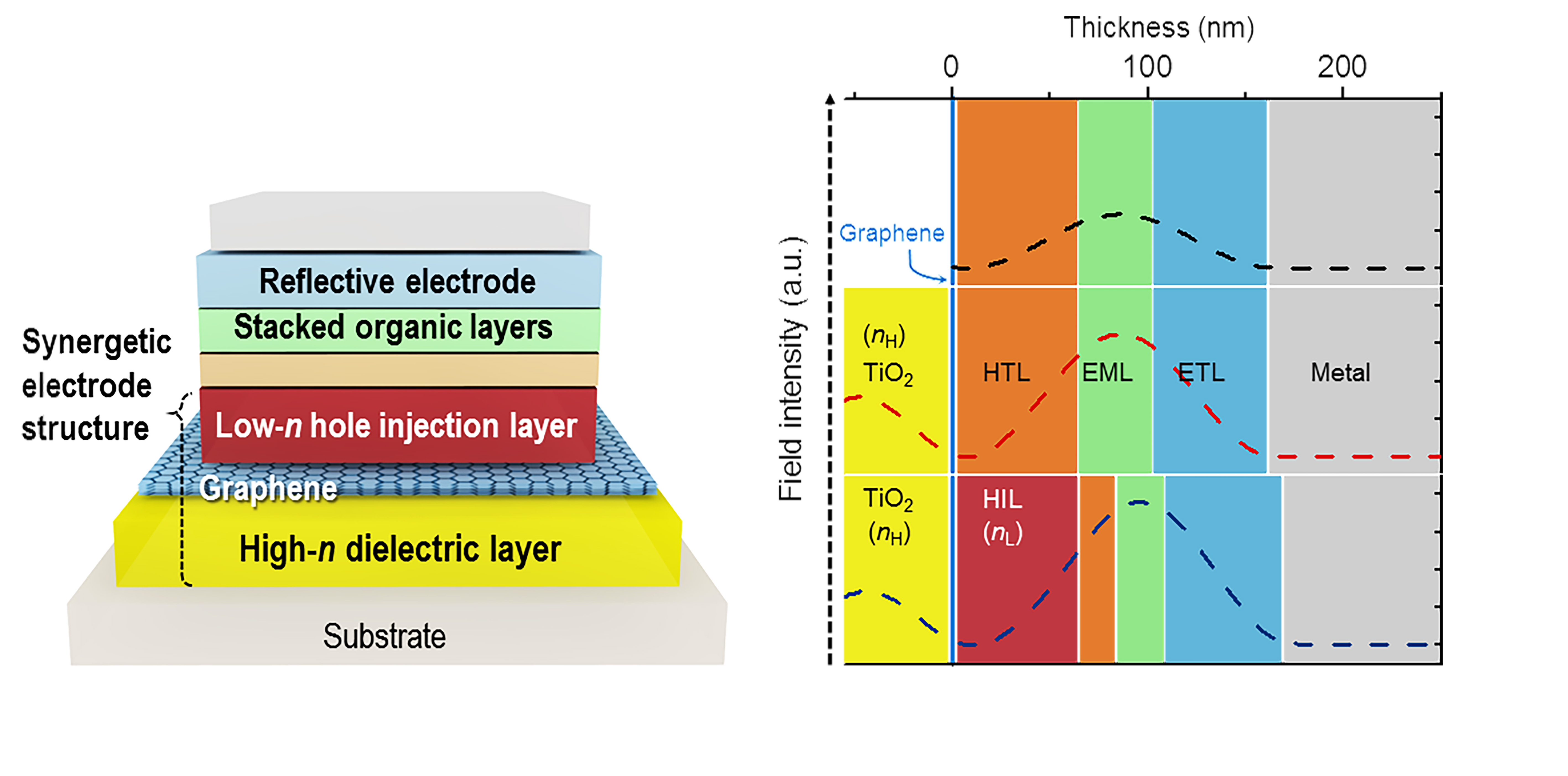
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
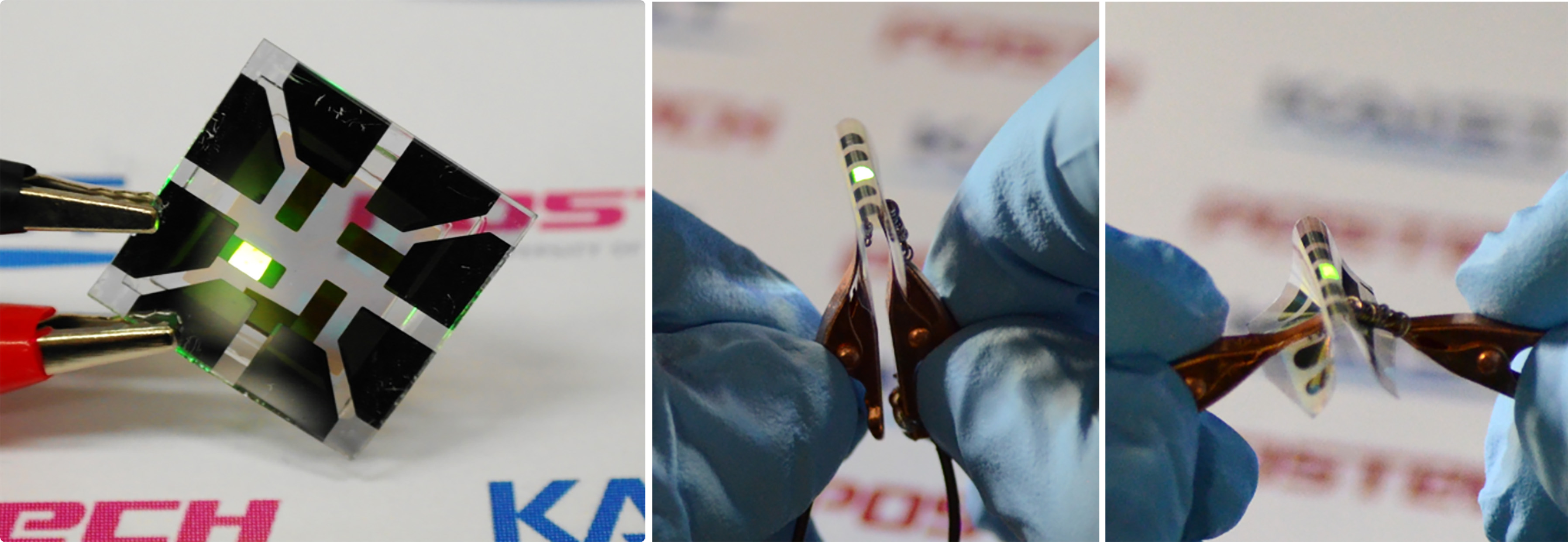
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).



 Next-generation Holographic Microscope for 3D Live Cell Imagi...
Next-generation Holographic Microscope for 3D Live Cell Imagi...